Main Page/BPHS 4090/Mapping a binding site using NMR spectroscopy
In this experiment, you will be using studying a fragment of a protein called CASKIN. It is involved in neuronal signaling. When a neuron is stimulated, chemical messengers are transferred between two neurons at a specialized cell-cell junction called a synapse. CASKIN is a scaffolding molecule found at the pre-synaptic side of the connection. A scaffolding molecule, much like its name, helps assemble other protein together in a certain part of the cell.
In the box below, draw a schematic of a synapse and the approximate location where CASKIN.
|
|
CASKIN is composed of many protein domains, each with its own function. Not suprisingly, since CASKIN’s job in the cell is to bring together other proteins, it is composed exclusively of domains that promote protein-protein interactions.
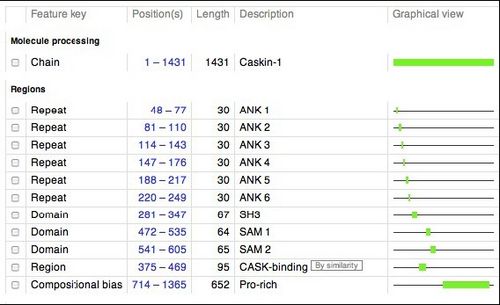
Below is a schematic of human CASKIN (1365 amino acids). This schematic was retrieved from the UNIPROT website (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WXD9), a respository of information on thousands of proteins. We will be studying the SH3 domain of CASKIN, found between amino acids 281 and 347 in the protein.
Members of the Donaldson laboratory used a technique called PCR to amplify the gene fragments encoding the SH3 domain, the first SAM domain, the second SAM domain, and the two SAM domains together. These fragments were inserted in to an expression vector, a circular piece of DNA or plasmid, that can be introduced into the common laboratory bacterium, Escherichia coli. Upon addition of a special kind of sugar into the culture which the bacteria cannot metabolize, the bacteria will begin to produce the human protein that we have programmed into them.
The cells were harvested and then cracked open. From the thousands of proteins in the bacterium the CASKIN SH3 domain was purfied in about two hours because it was tagged with a special sequence of six histidines that no other native bacterial protein had. Six histidines bind nickel very well so we used a special type of chromatography when nickel ions are exposed on a resin.
The protein was further purified by a technique called gel filtration that separated molecules according to their size. At this point the protein was extremely pure. It was then concentrated to about 10 mg /mL which doesn’t sound like much but it is !
From the NMR laboratory tour that you participated in, fill in the vital statistics of the CASKIN SH3 domain NMR sample:
|
|
length of NMR tube |