Difference between revisions of "Main Page/PHYS 4210/Mass Spectrometer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "<h1>Mass Spectrometer</h1> <p>The mass spectrometer is a device that separates and identifies ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio using the linear acceleration and defle...") |
|||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
<tr><td><b><sup>7</sup>Li</b></td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td></tr> | <tr><td><b><sup>7</sup>Li</b></td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td></tr> | ||
<tr><td><b>...</b></td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td></tr> | <tr><td><b>...</b></td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td><td> </td></tr> | ||
| − | </ | + | </table> |
Revision as of 12:17, 8 August 2011
Mass Spectrometer
The mass spectrometer is a device that separates and identifies ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio using the linear acceleration and deflection of ions, in electric and magnetic fields respectively.
|
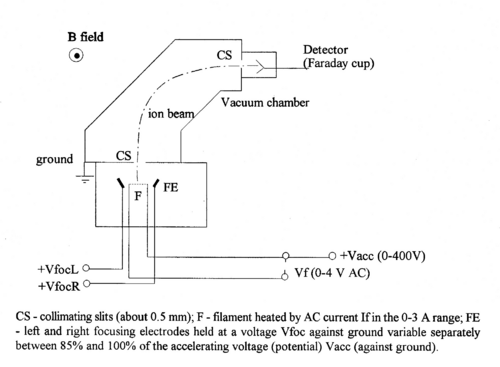
Figure 1 - Schematic diagram of the magnetic selector mass spectrometer.
|
Key Concepts
- Charge-to-mass ratio
- A/D Converter
- Mean free path
- Faraday Cup
- Diffusion pump
- magnetic selector
- Roughing pump
- Ion gauge
- Thermocouple gauge
Pre-Lab Requirement
This experiment has a prelab component. You must complete this exercise before you meet the TA for a demonstration.
Prepare a table of showing at which accelerating voltage you would expect to see a signal for the isotopes listed in the table below. Provide these for various values of magnetic field between 0.1T and 0.3T.
For example:
| 0.1 T | 0.12 T | 0.14 T | ... | |
| 1H | ||||
| 4He | ||||
| 6Li | ||||
| 7Li | ||||
| ... |