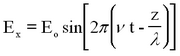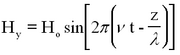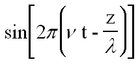Difference between revisions of "Main Page/PHYS 3220/Speed of Light"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<p>Light can be described as a periodic electromagnetic plane wave which carries energy in the form of an electromagnetic field. The electric and magnetic components can be written as:</p> | <p>Light can be described as a periodic electromagnetic plane wave which carries energy in the form of an electromagnetic field. The electric and magnetic components can be written as:</p> | ||
<table width=400 align=center><tr><td> | <table width=400 align=center><tr><td> | ||
| − | <p align=justify>[[File:C-eqn1.png| | + | <p align=justify>[[File:C-eqn1.png|180px|center]] |
</p> | </p> | ||
</td><td> | </td><td> | ||
| − | <p align=justify>[[File:C-eqn1b.png| | + | <p align=justify>[[File:C-eqn1b.png|180px|center]] |
</p> | </p> | ||
</td></tr></table> | </td></tr></table> | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 18 July 2011
Introduction
Light can be described as a periodic electromagnetic plane wave which carries energy in the form of an electromagnetic field. The electric and magnetic components can be written as:
This represents a monochromatic (single-frequency) beam travelling in the + z direction having a wavelength λ and frequency v (related by λ ν = c). The angle