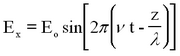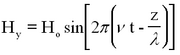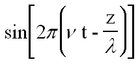Main Page/PHYS 3220/Speed of Light
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Introduction
Light can be described as a periodic electromagnetic plane wave which carries energy in the form of an electromagnetic field. The electric and magnetic components can be written as:
This represents a monochromatic (single-frequency) beam travelling in the + z direction having a wavelength λ and frequency v (related by λ ν = c). The angle
is called the phase of the plane wave. A point on the wave having a constant phase (e.g. the peak of a sine wave) moves at a velocity determined by setting the time derivative of the constant phase equal to zero